What is Corneal Collagen Crosslinking?
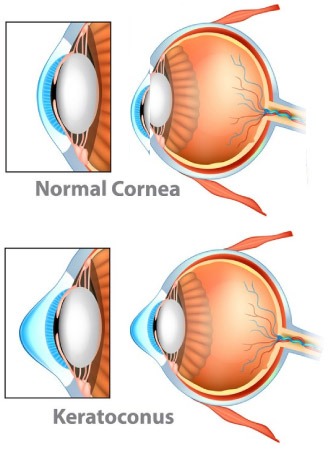
The Biomechanical properties of cornea are primarily determined by the collagen fibres and the degree of inter fibrillar linkage. Ectatic conditions of cornea may result from inflammation or they may be non inflammatory in origin. The non inflammatory ectasia are Keratoconus, Keratoglobus & Pellucid marginal degeneration, keratoconus being the most common Incidence of keratoconus in 8 general population is 1 in 2000. With the current diagnostic techniques the incidence is probably 1 in 600 to 1 in 420. It is more common in females and is usually bilateral. There is no specific hereditary pattern, but chances of a blood relative developing the disease is 1 in 10. It manifests at puberty and progresses slowly or rapidly over the next few years. In about 20% of the cases progression may be to an extent where corneal transplantation is required. The eitiology of this non inflammatory ectasia of the corneais unknown. Histopathology studies. reveal decreased number of collagen fibrils, membrane anomalies of keratocytes, fragmentation of the epithelial basement membrane, fibrillation and disintegration of Bowman’s membrane and degenerative changes of the basal epithelial cells. The treatment of this disorder has only been optical rehabilitation with RGP contact lenses, epikeratoplasty, intacs or keratoplasty. None of these treatment modalities can halt the progression of keratoconus. With the advent of C3R, for the first time there is hope for the millions of keratoconic patients, because this treatment can halt the progression of the disease.
Preoperative Work Up At Thind Eye Hospital
- Visual acuity Assessment uncorrected visual acuity, best-corrected visual acuity, best spherical corrected visual acuity, refraction, contrast sensitivity.
- IOP
- Detailed Slit lamp examination taking note of Vogts striae, Fleischer’s ring & corneal scarring
- Dilated fundus examination.
- Pentacam
- Slit lamp photographs of corneal changes and the lens.
- Central comeal thickness
- Thinnest pachymetry.
- Front KI (verticle), Avg. Front K2 (horizontal).
- Back KI (H), Avg. Back K2, (VM.
- SIM KISIMK2.
- Lens density,
- Apical elevation (F) (BFS and Float ON)
- Aberration Coeflicient,
- KKstage
- Corneal Topography: Axial Map, Mean Power
- (3MM), Minimum power, Maximum power,
- Symmetry index
- RNFLThickness (OCT)
- Foveal thickness (OCT)
FAQ's Related to C3 R
Crosslinking of human collagen is a physiologic process, stiffening of connective tissue is well known in diabetes and aging. Cross linking (X- linking) of the cornea is a new approach to increase the mechanical and biochemical stability of corneal tissue. The aim of this treatment is to create additional chemical bonds inside the corneal stroma by means of a highly localized photoploymerization while minimizing exposure to the surrounding structures of the eye. Several techniques are available to achieve X-Links in connective tissue, among others by means of, aldehydes, enzymes, and photo polymerization using UV-light. The most promising technique in cornea was found to be photo polymerization by means of a non-toxic and soluble photo mediator (riboflavin) and a wavelength which was absorbed strongly enough to protect deeper layers of the eye (riboflavin-VAtechnique
The 3 and 5 year results of the Dresden clinical study have shown that in all treated 60 eyes the progression of keratoconus was at least stopped (“freezing”). In 31 eyes there also was a slight reversal and flattening of the keratoconus by up to 2.87 diopters. Best corrected visual acuity improved slightly by 1.5 lines. So far, over 150 keratoconus patients have received corsslinking treatment in Dresden. (Gregor Wollensak Curr Opin Ophthalmol 17:356-360.©2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins). C3R holds potential for treatment of corneal melting lesions or superficial ulcers by increasing resistance to enzymatic lysis. Pretreatment of highly myopic patients with C38 before undertaking LASIK to minimize the chances of post LASIK ectasia could be another important use of this procedure. Patients with pre existing post LASIK keratectasia are also candidates for C3R. Simultaneous PRK & C3R of keratoconic patients to treat the cylindrical part of the refractive error would improve the spectacle tolerance of these patients. The potential uses of C3R could be innumerable but long term studies are needed to establish the same.
In general UV light has the potential to damage the cornea, the lens and the retina. UV exposure can cause photokeratitis, cataract formation and thermal or photo chemical damage in the retina. Furthermore the free radicals and oxidizing agents liberated during the procedure also pose a photo chemical risk to a nterior segment structures. Photokeratitis and sunburn are caused by UVB light (290-320nm) which is mainly 9 absorbed by the corneal epithelium. In crosslinking just a small peak-like sector of UVAspectrum (365nm) is used. The corneal absorption of UVA light is massively increased. due to the photosensitizer riboflavin, resulting in a UVA transmission of only 7% across the cornea. In the cornea the main issues are damage to the keratocytes and more.